While the EOR meaning might be unclear to some, for businesses seeking global growth, the Employer of Record model is a well-known solution — and for good reason.
When it comes to global expansion, the complexities of setting up local entities have impacted even some of the most successful global companies:
- Google settled with the French government for €965 million after the tax authorities demanded over €1 billion in back taxes due to improper labor law compliance;
- Apple faced a €13 billion back tax claim from the EU as a result of its inability to adhere to evolving local entity management and tax laws;
- Uber had to revamp its operational model entirely in the UK and reclassify drivers as employees, resulting in high operational costs and requiring a local entity.
As demonstrated, businesses set for global expansion or international hiring face numerous challenges — but that’s where the Employer of Record (EOR acronym) steps in.
So, what is an EOR? Check out this comprehensive guide on all the EOR essentials.
EOR Definition: Core Concept and Differentiators
The core goal of the Employer of Record is to simplify and streamline the employment process for businesses looking to expand their operations internationally.
Unlike the traditional process, where companies must set up a legal entity in the country, an EOR alleviates the burden of navigating complex local labor laws and administration.
EOR Definition
Employer of Record is a service provider dedicated to managing a range of legal, HR, and compliance-related tasks on behalf of its client company. Meantime, the client company retains control of the worker’s daily tasks and responsibilities.
To explore what makes the EOR model unique, see the table describing what is an Employer of Record approach and how it differs from the traditional expansion process.
| Aspect | Hiring through EOR | Traditional Hiring Process |
|---|---|---|
| Entity Setup | No need for local entities | Usually requires setting up local entities (depending on the location) |
| Employee Onboarding | 2-3 weeks | 2-6 months due to legal setup |
| Setup Costs | $6,000 – $25,000, including fees | $20,000 – $35,000+ |
| Scaling | – Immediate payroll setup – Pre-established compliance and contracts – Near-instant scalability within 2-4 weeks | – 4-12 weeks for payroll setup – 1-3 months for compliance and contract management – 6-12 months for scaling due to entity setup |
Why Use Employer of Record Services: Key Functions
The portfolio of EOR services spans multiple operations, from compliance to HR tasks and beyond. Let’s review them in more detail.
EOR Hiring & Onboarding
Scope of EOR work:
- The client company selects the employee they want to hire. Once the decision is made, the EOR hiring starts.
- As a part of the EOR staffing services, the Employer of Record takes care of employment contracts, ensuring they comply with the local labor laws and regulations.
- The EOR also manages the onboarding process, including employee registration with relevant authorities and tax bodies.
Why it matters:
The cost of a bad hire can be up to 30% of that employee’s annual salary, which EORs help mitigate by streamlining onboarding and legal compliance.
Hiring and Onboarding
Key Objective:
Potential Time Savings: 2-4 weeks per hire
Benefits:
- Employee selection by client
- Employment contracts
- Compliance with local labor laws
- Employee registration with authorities and tax bodies
- Work permits & visas
EOR Payroll and Benefits Management
Scope of EOR work:
- The Employer of Record payroll services include calculating salaries, deductions, and taxes according to local laws. Payments are made directly to the employee from the EOR.
- Apart from the Employer of Record payrolling, it also administers benefits such as health insurance, pension contributions, paid time off, and any other benefits required by local regulations or agreed upon with the client.
Why it matters:
Payroll errors affect 53% of US employees at least once in their careers, which EORs help reduce.
Payroll Management
Key Objective:
Potential Time Savings: 30-50 hours per payroll cycle
Benefits:
- Payroll processing
- Salary calculations and deductions
- Local tax compliance
- Direct salary payments
- Health insurance administration
- Pension contributions and benefits
EOR Health Insurance Coverage
Scope of EOR work:
- The EOR handles health insurance coverage as per the country’s labor laws.
- EOR compliance includes thorough research to adhere to various regional healthcare differences and ensure proper compensation for employees.
Why it matters:
With the average healthcare cost per employee in the USA around $15,000 per year, an EOR relieves a considerable burden of health insurance management by ensuring employees receive legally mandated benefits.
Health Insurance Coverage
Key Objective:
Potential Time Savings: 10-20 hours per month
Benefits:
- Public or private health plan enrollment
- Compliance with local health insurance regulations
- Administration of statutory benefits
- Disability insurance
- Pension and retirement contributions
Compliance and Legal Responsibility
Scope of EOR work:
- The EOR verifies whether the employment complies with local labor laws about minimum wage, working hours, leave policies, and termination requirements.
- They also manage tax reporting, submit required documents to tax authorities, and address Employer of Record tax implications.
Why it matters:
EOR reduces the risk of costly compliance-related fines and lawsuits that cost businesses up to $100,000 per violation.
Legal Compliance
Key Objective:
Potential Time Savings: 40-60 hours per compliance audit
Benefits:
- Adherence to labor laws (wages, hours, leave)
- Tax filings and social security contributions
- Compliance with government regulations
- Employee termination policies
- Employment law compliance
EOR Risk Mitigation
Scope of EOR work:
- The EOR takes on the legal risks associated with employment, such as non-compliance with labor laws, tax regulations, or employee lawsuits.
Why it matters:
With a strong focus on risk mitigation, EORs can help companies avoid costly legal disputes with an average of $75,000 per employee lawsuit in settlements.
Risk Mitigation
Key Objective:
Potential Time Savings: 20-50+ hours annually
Benefits:
- Legal risk management
- Non-compliance penalty mitigation
- Employee-related legal disputes
- Protection against lawsuits and legal penalties
- Risk reduction of labor law non-compliance
Tax Management and Reporting
Scope of EOR work:
- The EOR’s knowledge of local laws guarantees that income taxes, social security contributions, and other statutory withholdings are properly deducted from employee paychecks.
- Thanks to the Employer of Record tax implications are made easy: EORs manage tax reporting, submit required documents to tax authorities, and ensure the client company remains compliant with local tax obligations.
Why it matters:
While the average business spends about 60 hours per year on tax-related tasks, EORs can significantly streamline this process.
Tax Management & Reporting
Key Objective:
Potential Time Savings: 30-40 hours annually
Benefits:
- Tax withholding from paychecks
- Social security contributions
- Local income tax compliance
- Annual tax filings and reporting
- Ensuring adherence to local tax obligations
Employment Contract Management
Scope of EOR work:
- The EOR employment contract management settles all employment terms: compensation, benefits, working conditions, etc.
- The EOR also handles any Employer of Record contract renewals or amendments for the client.
Why it matters:
In many countries, failure to comply with employment contract laws can result in fines of up to $20,000 per infraction.
Contract Management
Key Objective:
Potential Time Savings: 10-15 hours per contract cycle
Benefits:
- Employment contracts drafting
- Contract renewals and amendments
- Compliance with local labor regulations
- Defining compensation, benefits, and working conditions
Human Resource Management
Scope of EOR work:
- The EOR takes over all HR administration workload, from employee contracts to worker classification to essential local documentation.
- EOR HR support is also provided whenever there are any employee disputes or legal consultations needed.
Why it matters:
EORs can reduce the time it takes to hire globally by 50%, compared to managing international hires in-house.
HR Management
Key Objective:
Potential Time Savings: 20-30 hours per month
Benefits:
- Employee contracts and classification
- Worker classification (full-time, part-time, contractors)
- HR support (employee disputes, disciplinary actions)
- Legal consultations
- Employee record management
Termination and Offboarding
Scope of EOR work:
- Whenever the company decides to terminate an employee, EORs handle the process. They ensure compliance with local laws while considering important factors such as notice periods, severance pay, and legal protections.
- The EOR also manages the entire offboarding process, ensuring all final payments, benefits, and legal requirements are met.
Why it matters:
Improper employee termination can result in wrongful termination lawsuits, averaging $40,000 in settlement costs.
Termination & Offboarding
Key Objective:
Potential Time Savings: 10-15 hours per termination case
Benefits:
- Employee termination process
- Final payments and settlements
- Offboarding administration
- Compliance with local termination laws
- Legal risk management during offboarding
Check Reviews of Leading EOR Providers
Employer of Record Pros and Cons, Impact, Use Cases
Typical EOR Use Cases
To better understand why use an Employer of Record services and assess the Employer of Record benefits and impact, let’s imagine and review common expansion scenarios:

EOR Benefits
Opting for the Employer of Record provider, businesses across any industry or region can witness game-changing EOR benefits, such as:
Quick Hiring and Onboarding
Since EOR manages local hiring and all employment regulations, it speeds up the commonly tedious market entry to a matter of weeks.
Employee Mobility
The EOR takes care of work permits and visas for the relocated employees as per immigration laws, streamlining the expansion and saving the company from potential fines.
Risk Mitigation
The Employer of Record risk mitigation strategy covers everything from potential compliance pitfalls to risk management strategy and monitoring.
Scalability
With EOR-powered remote team management, the workforce can be scaled up easily whenever needed and without administrative hurdles.
Cost Efficiency
Due to the EOR’s efficiency and the actions mentioned above, businesses can fully avoid the costly expenses otherwise spent on establishing a local subsidiary.
The benefits of EOR are numerous; however, there are also potential pitfalls associated with the EOR model. How valid are these concerns, and if so, how can they be minimized? Let’s review them in detail.
Key EOR Benefits and Challenges
- Quick hiring and onboarding
- Employee mobility
- Risk mitigation
- Compliance assurance
- Administrative burden relief
- Simplified global expansion
- Scalability
- Cost efficiency
- More complex communication workflows
- Less cultural alignment
- Potential over-reliance on the EOR
- Compliance assurance
- Potential difficulties in EOR termination
- Higher upfront costs, service fees
- Limited control
- Greater expenses for long-term commitments
EOR Considerations
Must-know considerations when hiring an EOR include:
Complex Communication Workflows
Due to the fact that EOR serves as a middleman between the company and the employee, there is a belief their communication might become more layered and slower.
How to solve: To minimize this, companies can establish clear communication protocols and regular check-ins with the EOR to ensure efficient and transparent workflows.
Less Cultural Alignment
Since the EOR is the legal employer, employees may feel less connected to the company’s culture, which might create a gap in fostering strong team bonds and shared goals.
How to solve: With the EOR handling administrative tasks, companies can focus on fostering culture by integrating EOR-hired employees through team-building activities, virtual meetings, and inclusive communication.
Potential Over-Reliance on the EOR
Companies that do not oversee the level of control they pass to the EOR may become overly dependent on its services, thus facing some challenges if they decide to switch EOR providers or transition to a local entity.
How to solve: While the majority of tasks are passed to the EOR, businesses still need to keep an eye on their HR processes and stay in the loop with the most important updates. Plus, contingency plans can help ensure a smoother transition when needed.
Permanent Establishment Risks
For some business scenarios, associated Employer of Record risks imply that using an EOR in certain jurisdictions could trigger “permanent establishment” (PE) status, resulting in additional tax liabilities for the company.
How to solve: Regularly reviewing operations and local laws, along with working closely with tax advisors and legal experts, can help avoid potential tax liabilities.
Potential Difficulties in EOR Termination
Ending an EOR relationship might be complicated, especially when transferring employees to direct contracts and navigating local laws for termination or transfer procedures.
How to solve: Working with legal teams, setting clear timelines, and understanding local employment laws will help ensure a smooth termination process and avoid legal issues.
Higher Upfront Costs, Service Fees
Some EOR services are charged by the employee, which increases upfront costs. Over time, these fees can accumulate, making the EOR model more expensive than setting up a local entity.
How to solve: Compare EOR fees with the cost of establishing a local entity and choose the most cost-effective option based on your long-term goals. For short-term or smaller teams, EOR may still be more efficient.
Limited Control
Since the EOR handles HR, legal, and compliance work, companies may find themselves with quite limited direct control over these processes.
How to solve: Set clear expectations with the EOR provider upfront, outlining key policies and processes. Maintain regular communication and conduct periodic reviews to ensure alignment on HR compliance policies.
Greater Expenses for Long-Term Commitments
EOR services are often considered more suited for short- to mid-term solutions. Over time, EOR fees may become cost-prohibitive for companies with a permanent regional presence.
How to solve: Conducting a thorough, regular cost-benefit analysis can help identify the tipping point where setting up a local entity becomes more financially viable.
Discover the top Employer of Record companies to find the right fit for your global hiring needs.
Role of Employer of Record in Fueling Global Expansion
The EOR hiring process is designed to be a smooth collaboration between your business and the EOR provider, with the shared goal of streamlining international hiring. So, how does EOR work? Let’s review the process step by step.
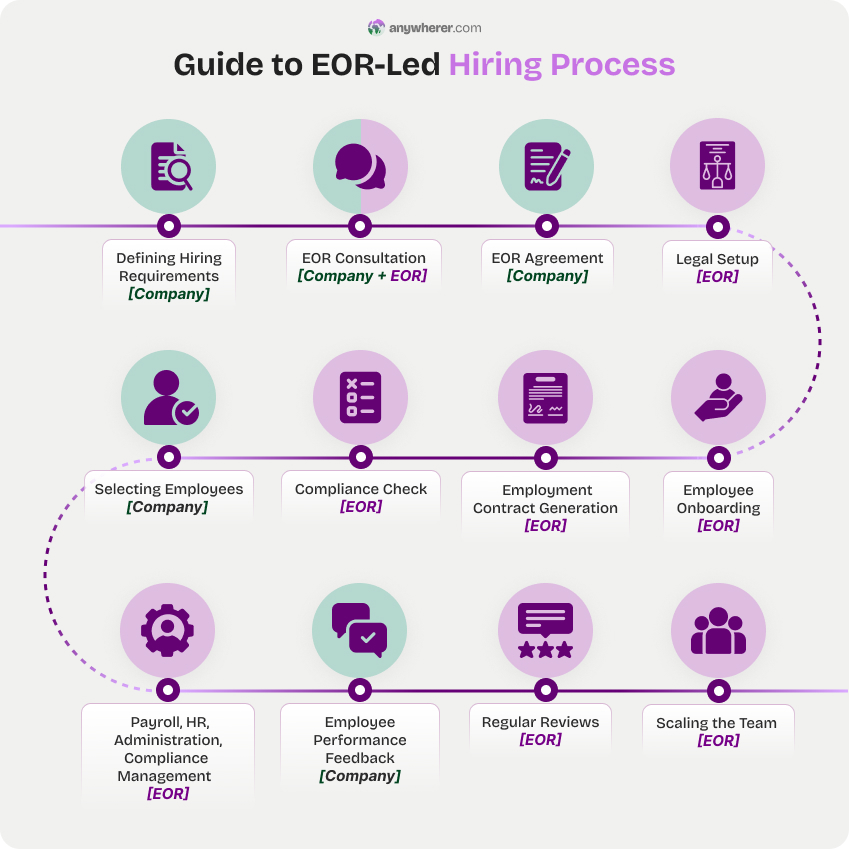
- Defining hiring requirements. The company identifies the position, qualifications, and the country where the employee will be hired.
- EOR consultation. The EOR discusses the client’s needs, local employment laws, and necessary compliance factors.
- EOR agreement. At the Employer of Record agreement stage, the company opts for an EOR provider, reviews service packages, and finalizes the contract outlining responsibilities, fees, and services.
- Legal setup. The EOR sets up the framework for managing employment in the desired country.
- Selecting employees. The company recruits and selects the candidate(s) they want to hire.
- Compliance check. The EOR ensures that the offer and contract comply with local labor laws and regulations.
- Employment contract generation. The EOR prepares employment contracts that adhere to the country’s labor laws, including compensation, benefits, and working conditions.
- Employee onboarding. The EOR manages the onboarding process, including registering employees with relevant tax and social security authorities.
- Payroll, HR, administration, and compliance management. The EOR oversees payroll, manages day-to-day HR tasks, and ensures adherence to local compliance.
- Employee performance feedback. The company provides regular feedback on the employee’s performance, while the EOR manages the administrative side of employment.
- Regular reviews. The EOR conducts regular check-ins with the client to ensure satisfaction and compliance, offering adjustments as necessary to accommodate business changes.
- Scaling the team. The EOR can scale up or down the workforce as needed, offering flexible solutions based on business demands.
Employer of Record Pricing Models
Employer of Record services come with different EOR pricing models, each designed to accommodate varying business needs and make the EOR cost viable for both small startups and large-scale enterprises.
EOR Pricing Models
| Per Employee per Month (PEPM) | Percentage of Employee Salary | Flat Fee | One-Time Setup Fee |
| Flexibility: High Scalability: High Cost: Medium | Flexibility: Medium Scalability: High Cost: High | Flexibility: Low Scalability: Medium Cost: High | Flexibility: Low Scalability: Low Cost: Low |
| Tiered Pricing Model | Pay-as-You-Go | Customized Pricing | |
| Flexibility: High Scalability: High Cost: Medium | Flexibility: High Scalability: High Cost: High | Flexibility: High Scalability: Medium Cost: Medium |
Per Employee per Month (PEPM)
With this model, you’ll pay a consistent, flat monthly fee per employee. This way, it’s great for its predictable and straightforward billing that makes financial planning easier for companies.
However, the model has its downside: as the number of employees grows, it can become less cost-efficient.
- Ideal for: companies looking for predictable, recurring billing.
- Downside: the risk of becoming expensive for large teams.
Percentage of Employee Salary
Under this model, the EOR cost is based on employee compensation and is calculated as a percentage of each employee’s gross salary.
The option is great for those seeking flexibility. However, note this: if you’re looking for highly skilled or niche employees who have to be highly compensated, your EOR costs will go up significantly.
- Ideal for: organizations with a fluctuating payroll cost structure that require flexibility.
- Downside: not efficient for hiring high-skilled workers.
Flat Fee
The flat fee model charges a fixed amount per month, regardless of any other factors. Constant and predictable costs are the key benefits, but they come at the expense of flexibility.
- Ideal for: small teams or short-term projects.
- Downside: lack of flexibility makes it inefficient when scaling the workforce.
One-Time Setup Fee
With this model, you pay a one-time fee for onboarding each new employee. This cost covers payment for tasks like legal compliance, contracts, and payroll setup.
The one-time setup fee is ideal for businesses with short-term projects or minimal hiring, as they only pay for onboarding once. However, upfront costs can be significant, especially when scaling rapidly or hiring large numbers of employees.
- Ideal for: short-term projects or minimal hiring.
- Downside: upfront costs, including one-time setup fee and others.
Tiered Pricing Model
With this model, the cost per employee decreases as you hire more staff. For companies set for exponential growth, this allows them to save money as their workforce expands. Meantime, for those with fewer employees and limited hiring needs, the model will not be as advantageous.
- Ideal for: large teams or companies planning to scale.
- Downside: smaller companies may not benefit as much.
Pay-as-You-Go
This model charges companies based on the specific services used, which can be ideal for businesses that need certain services based on specific demand.
However, note that this flexibility comes with unpredictability, and costs can fluctuate from month to month. Thus, companies often find it harder to budget for ongoing expenses.
- Ideal for: companies needing flexibility for specific tasks.
- Downside: monthly expenses may be hard to predict.
Customized Pricing
This model is tailored to fit the unique business requirements. While highly flexible, it requires more commitment to discussing and managing contractual arrangements, which adds time and complexity to the setup process.
- Ideal for: companies with complex or unique hiring needs.
- Downside: requires negotiation and more detailed arrangements.
EOR Cost: An Investment That Pays Off
Because EORs provide a cost-effective, efficient, and low-risk way for companies to expand globally and manage international employees, it has become the choice for many renowned companies like Deloitte, Microsoft, Revolut, OpenAI, TOYOTA, Asus, Rakuten, Zoom, and many others. So, is it worth the investment? While the answer depends on your company’s goals, market complexity, and other factors, EOR offers significant advantages in many scenarios.
Cases When EOR Is a Perfect Fit
- You want to focus on business growth while outsourcing HR tasks
- You want to minimize the challenges of legal and payroll management
- You plan for short-term projects without long-term entity setup
- You prioritize the speed of hiring
- You take local compliance seriously
Summing up, the EOR model is a good fit for numerous businesses, offering the benefits of quick, compliant global expansion without the need to set up a legal entity. For businesses that consider other expansion options, there are alternatives such as PEO, outsourcing, and subsidiaries — yet, when compared side-by-side, EOR excels in several key areas.
| EOR | PEO | Outsourcing | Subsidiary | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No need for legal entity | ✔ | X | ✔ | X |
| Employment process management | ✔ | X | ✔ | ✔ |
| Employee management | ✔ | ✔ | X | ✔ |
| HR services | ✔ | ✔ | X | ✔ |
| High speed of hiring | ✔ | X | ✔ | X |
| Ease of scaling | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | X |
| Compliance management | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Level of control | Limited | Moderate | Low | No need for a legal entity |
Frequently Asked Questions about EOR
What do EORs support and benefit businesses?
An Employer of Record (EOR) manages a company’s legal and administrative responsibilities in employing workers in another country. EORs handle payroll, taxes, HR tasks, employee benefits management, and compliance with local labor laws. This allows businesses to expand internationally or hire remote talent without setting up a local legal entity, enabling faster and more cost-effective global hiring.
How much does an Employer of Record cost?
The average cost varies on the construction of expenses. The first one is how difficult the administrative load and the regional operation are – whether it’s mere payroll outsourcing or a comprehensive global expansion strategy. Also, the total number of employees, locations, and pricing model workforce and influence the eventual cost.
Do employees work for you or for the Employer of Record? Will you lose control over your employees?
While the EOR is the legal employer on paper, handling compliance and administrative tasks, your company retains full control over day-to-day operations, work assignments, and management decisions. The EOR simply handles the backend processes, serving as a workforce management solution that covers your needs. Thus, you won’t lose control over your employees; instead, you’re free from the burdens of HR and legal paperwork.
Employer of Record vs contractor: what option is the winning one?
The choice between using an international Employer of Record or hiring contractors depends on your business needs. An EOR is ideal if you need to hire full-time employees and comply with local labor laws while maintaining long-term control over the workforce. Contractors are better suited for short-term projects or roles that don’t require the benefits and protections afforded to full-time employees. However, using contractors for long-term needs can risk misclassification and legal issues in some countries.
How does an EOR differ from a PEO?
An EOR assumes full legal responsibility as the official employer of your employees while you manage daily operations. On the contrary, A PEO (Professional Employer Organization) operates under a co-employment model, meaning both the client company and PEO share employer responsibilities. The PEO requires you to have a local legal entity, while the EOR does not, making remote Employer of Record providers better for companies without a local presence.
Is it safe to use the Employer of Record?
Yes, using an EOR is generally considered safe and is a legally accepted practice in most countries. A reputable EOR ensures full compliance with local labor laws. However, it’s essential to select a trustworthy provider to avoid potential pitfalls, like tax compliance risks or service delays.
What things should you keep in mind while choosing an EOR solutions provider?
When looking for an EOR provider, consider these factors: reputation, experience, compliance expertise, and global reach in your target countries, to name a few. Review their cost structure to fit your budget and long-term needs. Besides, the process of finding an Employer of Record must include checking their service offerings, communication methods, and reviews from former clients. You can also use a trusted EOR platform to compare the providers.
Navigate your way to global growth with EOR: simplify the complexities of international hiring in a fraction of the time with near-zero effort!

Yaryna is our lead writer with over 8 years of experience in crafting clear, compelling, and insightful content. Specializing in global employment and EOR solutions, she simplifies complex concepts to help businesses expand their remote teams with confidence. With a strong background working alongside diverse product and software teams, Yaryna brings a tech-savvy perspective to her writing, delivering both in-depth analysis and valuable insights.











