What’s Behind the PEO Meaning?
PEO streamlines HR for businesses by managing essential functions like payroll processing, ensuring employees are paid accurately. They provide access to competitive employee benefits and help companies stay compliant with labor laws, reducing legal risks.
With a comprehensive suite of responsibilities and global PEO coverage, this approach enables the client company to focus on its core business operations while cost-effectively handling HR functions.
PEO Definition
A Professional Employer Organization (also known as PEO acronym) acts as a co-employer for its clients while offering a comprehensive suite of HR solutions to help companies manage employee-related administrative functions.
As per a Professional Employer Organization definition, PEO functions as a co-employer taking over the legal share of responsibilities. This way, the PEO model encompasses the responsibility of co-managing a variety of HR functions. Additionally, international Professional Employer Organizations are committed to providing global HR coverage across multiple countries and ensuring compliance with diverse local employment laws and regulations.
Main Areas of PEO
Payroll Processing

Employee Benefits Administration
Compliance Management

Human Resources Support

Risk Management

Recruitment and Staffing

Training and Development

Performance Management

Time and Attendance Tracking
PEOs come in different forms and accreditations. For instance, a CPEO (short for Certified Professional Employer Organization) is a PEO that has received IRS certification, providing additional tax benefits and assurances for compliance. Unlike a standard PEO, a CPEO’s certification ensures the IRS recognizes it as a legitimate co-employer, adding an extra layer of trust and tax advantages for clients.
While exploring PEO meaning, it’s also important to understand EOR meaning (Employer of Record). While both solutions help businesses manage HR, payroll, and compliance, an EOR takes full legal responsibility for employees in international markets, whereas a PEO partners with companies that already have legal entities in place.
For a deeper understanding of how the PEO model works in practice, check out our detailed TriNet review for insights into its services and performance.
PEO Model in 2025: Does It Still Matter?
The main purpose of PEOs is to help their clients focus on their core competencies while they tackle HR complexities. But how does this align with current business realities? Let’s examine whether PEOs can effectively address today’s most critical business and HR-related challenges.
Addressing Economic Uncertainty
Fluctuating markets, inflationary pressures, and geopolitical disruptions all contribute to the challenges associated with economic turmoil.
During these unpredictable times, many companies are looking for ways to remain agile and cut costs without sacrificing the quality of their workforce. A global Professional Employer Organization is one of such solution, offering comprehensive HR, payroll, and compliance support. For businesses that prefer to retain full control over employment while outsourcing administrative tasks, an Administrative Services Organization (ASO) can be an alternative approach.
Where PEO steps in:
- Streamlining HR functions, compliance, and access to cost-effective employee benefits.
- Allowing companies to remain agile thanks to a scalable workforce and multi-faceted HR services coverage.
- Mitigating risks associated with economic uncertainty through shared liability and scalable workforce solutions.
Empowering Shift towards Remote Work
The fast-tracked transition to remote work, driven by the pandemic, has opened up opportunities to hire talent from anywhere in the world.
However, such change has also introduced new complexities in managing remote teams, particularly concerning compliance, payroll, and benefits in different jurisdictions.
Where PEO steps in:
- Managing globally distributed teams, including their payrolls, benefits, and other related HR responsibilities.
- Navigating cross-border employment compliance to avoid potential fines in other countries.
- Streamlining onboarding and payroll for remote workers worldwide.
Fighting Current HR Operational Challenges
With 56% of small businesses lacking a dedicated HR department — and 27% of those having only one HR staff member — companies often struggle with effective talent management.
This goes far beyond the SMB sector, with even 26% of Fortune 100 companies not having Human Resources represented in the C-Suite. Without strategic HR oversight, organizations face various challenges — and compliance is at the top of the list.
Where PEO steps in:
- Providing access to competitive benefits packages, which allows for enhanced employee satisfaction and retention.
- Allowing for scalable workforce solutions with the possibility for adjustments based on demand.
- Simplifying talent management with onboarding and training resources.
What a PEO Can Do: PEO Benefits, Impact, and Use Cases
Any decision to choose a PEO partner requires a thorough review of its offerings and potential impact. Let’s examine a Professional Employer Organization pros and cons, as well as its range of capabilities, in greater detail.
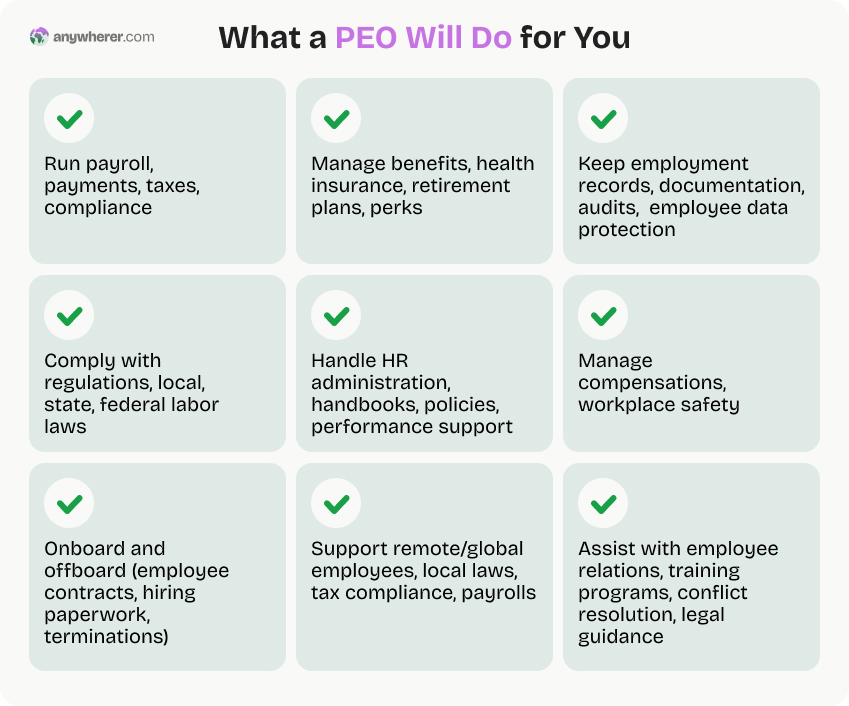
Keeping the above-mentioned benefits of using a PEO, there are certain areas where PEOs can bring the most impact for businesses. Let’s review them in detail.
You will benefit from a PEO if:
You look for cost-effective benefits
Since PEOs pool employees across their client base. Thus, PEO for small business provides the advantage of an access more affordable Professional employer Organization health insurance, retirement plans, and other employee benefits typically reserved for larger companies.
Your aim at reducing administrative burden
By handling time-consuming HR tasks like payroll, benefits administration, and compliance monitoring, PEOs help businesses focus on their core business activities without wasting time on administration. This frees up the companies’ internal resources and fosters strategic improvements and growth.
You lack in-house HR expertise
Many small to mid-sized businesses don’t have a dedicated HR department. PEO for startups fills that gap by providing professional HR support, offering all necessary services to ensure your HR processes run smoothly.
Your business is facing rapid growth
One of the key PEO benefits is that it can quickly adapt to workforce changes. They provide the necessary HR infrastructure — so that, whether you’re adding a few employees or growing by the hundreds, a PEO HR service ensures compliance and smooth integration and reduces the risk of costly errors or delays.
Your business operates in multiple states or countries
Managing compliance following various geo-based regulations can take a lot of work for businesses operating in multiple locations. PEOs simplify this by ensuring compliance with state-specific employment laws, payroll taxes, and workers’ compensation requirements. This way, PEO risk management reduces the potential of penalties and legal issues that arise from non-compliance.
You have a diverse employee group
If your workforce includes employees in different states, regions, or with varying employment needs (e.g., full-time, part-time, remote), a PEO firm helps manage this complexity. By pooling employees, PEOs can secure lower average healthcare costs, offer flexible benefit plans, and ensure all workers have the coverage they need.
You’re a small-size business
Smaller businesses with under 100 employees can achieve substantial savings on employee benefits, like health insurance and retirement plans. These offerings are typically more expensive for smaller companies to secure independently.
Meantime, note this: larger teams can also benefit from PEOs, especially in streamlining HR processes and ensuring compliance. While costs may be higher, the added value often justifies the expense.
PEO HR and the Global Workforce
PEOs support HR teams in focusing on core business goals while ensuring legal compliance in global operations — a scope that is often undervalued. Local laws and regulations vary distinctly across countries, hence the added complexities for the HR teams is immense. These differences span multiple aspects of recruitment and HR management, including:
- Employment contracts
- Benefits compliance
- Payroll and tax compliance
- Termination and severance requirements
- Working hours and overtime
- Visa and work permits
- Work council and employee representation
- Data privacy and security
To illustrate the wide-ranging variables, see the table below — highlighting key regulatory differences across various countries that PEO staffing services can efficiently manage.
| Geo-Based Requirements | |||
| Japan | |||
1) Mandatory health insurance & pension benefits | 2) Restrictive termination laws favoring employee retention | 3) Working hour limits enforcement | 4) APPI for data privacy |
| Australia | |||
1) Superannuation contributions | 2) Adherence to The Fair Work Act | 3) Strict overtime regulations | 4) Temporary Skill Shortage visas for foreign workers |
| Canada | |||
1) Mandatory fees for Employment Insurance and the Pension Plan | 2) Employee entitlement to severance based on provincial laws | 3) Labor Market Impact Assessments (LMIA) may be required | 4) 1.5x the regular pay rate for hours worked beyond 40-44 hours |
| Germany | |||
1) Work Council required for companies with 20+ employees. | 2) Social security, health insurance, and pension contributions required | 3) Detailed labor standards and payroll regulations. | 4) GDPR compliance for data privacy |
Before Opting for PEO Agency: Things to Consider
While the scope of work and PEO advantages are extensive, this option has its limitations that allow employers to retain control over operational oversight and strategic HR decisions.
Remember: PEO is a co-employer relationship, but you call the shots when it comes to the strategy. Hiring choices, performance management, and building company culture are all the company’s responsibilities that PEOs do not control. Also, while PEOs offer compliance guidance, they do not serve as legal counsel or set pay levels, leaving compensation and conflict resolution to the business itself.
PRO TIP: Ensure double-checking after engaging with a PEO agency: as they act as a middleman, it’s important to verify that no mistakes are made. After all, you know your business and employees better than they do, and there may be specific nuances to consider.

PEO Pitfalls and the Ways to Avoid Them
Like any business relationship, working with a PEO comes with potential challenges. Let’s explore the Professional Employer Organization disadvantages and potential pitfalls and how to steer clear of them throughout the PEO collaboration.
Unclear pricing
While PEOs may offer appealing initial rates, some agencies have complex pricing structures and even hidden fees: renewal rates, administrative charges, additional costs for extra services — the list can go on and on. Considering this, seeing a clear breakdown of what you’re paying for might be not that easy, especially for companies that are not used to clarifying every detail.
How to address:
- Request a detailed cost breakdown during negotiations.
- Consider negotiating service agreements to include specifics about pricing adjustments you can benefit from, such as caps on annual price increases or fixed rates for key services.
Exit costs
If you view a PEO as a temporary or short-term solution, consider that exiting a PEO can be costly — commonly, penalties or additional fees associated with termination can add up quickly. Also, since your company will switch to handle employee benefits management and compliance in-house, it will take additional costs for your business.
How to address:
- Carefully review the exit clauses and penalties before entering into a contract.
- Plan for contingencies by discussing potential exit strategies with the PEO in case you decide to part ways.
Lack of personal touch
Since a PEO is unfamiliar with your business and employees, working with a PEO provider can sometimes create a sense of disconnect for employees, especially when they’re directed to contact general hotlines for questions like payments, social benefits, or any HR-related issues.
How to address:
- Foster direct communication between employees and your internal HR team for personalized support.
- Familiarize a dedicated PEO representative with your company values.
The potential occurrence of mistakes
PEOs may not be familiar with the specific needs of your business and its employees, which can result in occasional mistakes. Thus, it’s crucial to double-check their work to avoid complications.
How to address:
- Establish regular check-ins with your PEO to review processes and correct any issues.
- Create a checklist of common tasks to monitor and verify accuracy.
Limited customization
PEOs often provide a set of standard policies and a boilerplate employee handbook, which may not suit every organization. If your HR and finance teams are well-developed, you might find yourself paying for services you don’t need due to the one-size-fits-all approach.
How to address:
- Clearly communicate your specific needs and preferences during onboarding
- Request customization options for your specific business case.
Key Practices to Ensure Successful PEO Services Integration
When working with PEO, make sure to follow these practices:
Clarify in utmost detail the worksite agreement you have with the PEO
Ensure you have a clear understanding of the role division between you and the PEO to avoid operational gaps. Since, in most cases, business decisions remain the company’s responsibility, be prepared to stay involved in strategic decisions and integrated into key processes.
Dig into the customer service model
Verify the scope of customer services the PEO is committed to providing. If a dedicated account representative is promised, confirm their accessibility, response time, and support hours. Also, check if they assist both administrators and employees — this will help you gain a clear perspective on future collaboration and processes.
Take advantage of PEO’s HR training
Many PEOs offer consultants and on-demand HR training, guiding on issues of varying complexity. This advantage is worth utilizing, especially as HR laws change nearly every year.
Look for local PEO companies, but consider scalability
While their rates are similar, smaller local PEOs often provide better support and personalized interaction than larger companies, which may outsource services or experience high turnover. A regional PEO may work well initially but could become limiting as your business grows beyond its coverage. Therefore, ensure your PEO can support expansion into other priority regions.
Check certifications
PEO holding CPEO and ESAC certifications indicate they are IRS-approved and meet high standards for financial security, compliance, and operational reliability. This will provide added confidence in its ability to manage clients’ operations accurately and responsibly.

How Does a PEO Work?
So, with all aspects above considered, how does a Professional Employer Organization work?
The Professional Employer Organization (PEO) process focuses on co-employment, where both the company and the PEO share responsibilities for managing employees. Here’s an overview of how PEO works, step by step.
| Without PEO | With PEO | |
| Hiring Needs Specification | The company meets internally to discuss hiring needs | Meet with PEO to outline goals and challenges |
| Defining Job Requirements | HR defines job roles and responsibilities | Company collaborates with PEO to define roles |
| Job Posting and Recruitment | Managed by HR | Managed by PEO |
| Candidate Sourcing | HR sources candidates | PEO leverages its network for candidate sourcing |
| Candidate Screening | Managed by HR | Managed by PEO |
| Selection of Candidates | Final selection made by HR and management | Company retains final say but PEO assists |
| Employment Contract Generation | Managed by HR | Managed by PEO |
| Onboarding Process | Managed by HR | Managed by PEO |
| Payroll Setup | Managed by HR | Managed by PEO |
| Compliance Management | Managed by HR | Managed by PEO |
| Benefits Administration | Managed by HR | Managed by PEO |
| Workers’ Compensation Management | Managed by HR | Managed by PEO |
| Ongoing Support | Managed by HR | Managed by PEO |
| Regular Performance Reviews | Managed by HR | Managed by PEO |
Getting Started with PEO Partner: Step-by-Step Guide
For companies that have already decided to opt for a PEO and are wondering what the initial steps look like, we’ve got you covered.
From assessing your business needs to understanding the roles and responsibilities in the worksite agreement, this guide covers the essential steps to help you make a smooth transition to PEO-supported operations.
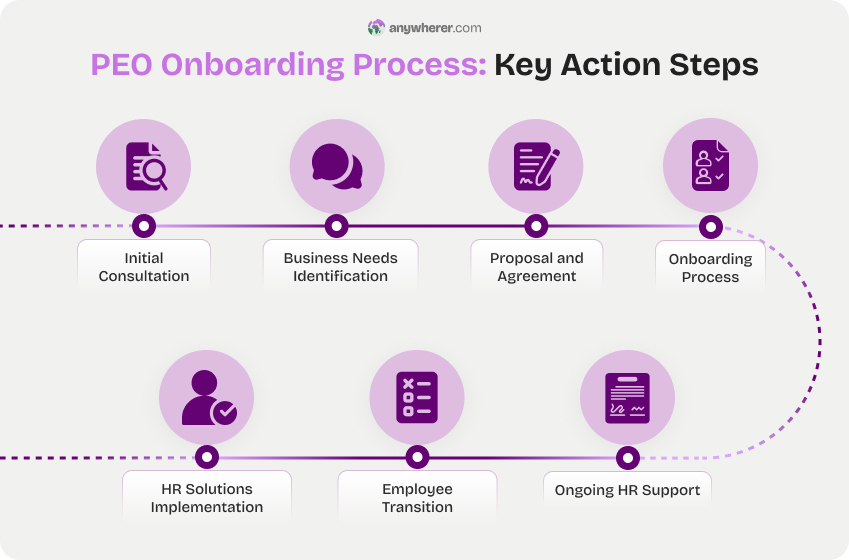
- Initial consultation. The company meets with PEO representatives to discuss your business needs, goals, and challenges.
- Business needs identification. The company identifies its current operational gaps by evaluating its HR functions, employee benefits, and compliance status.
- Proposal and agreement. The company reviews the PEO’s proposal, including services offered, pricing structure, and the worksite agreement.
- Onboarding process. The company prepares necessary documentation and employee information for onboarding. At this stage, a dedicated PEO representative is assigned to them.
- HR solutions implementation. PEO benefits administration, payroll processing, and compliance management systems are set up at this stage, along with creating or customizing employee handbooks and HR policies.
- Employee transition. At this step, the company notifies its employees about the PEO partnership. Next on, they conduct a dedicated meeting together to explain the changes and address concerns.
- Ongoing HR support. PEO handles HR consulting, training, employee development resources, and compliance, while the company oversees the process. Whenever needed, regular reviews are scheduled to assess performance, address issues, and make adjustments according to the company’s evolving needs.
PEO Pricing Models
Coming in various sizes and packages, Professional Employer Organization price can vary based on numerous factors. Explore a PEO cost comparison and examine business scenarios where each model may be the best fit.
Percentage of Payroll
With this model, the PEO’s fees are based on a percentage of the total payroll, typically ranging from 2% to 10%. This percentage adjusts as payroll expenses change.
Since this PEO payroll model allows flexibility as the company scales, it is well-suited for businesses with consistent payroll costs. However, the fees will grow with salary rises or additional hires.
- Ideal for: businesses that have stable payroll costs.
- Downside: fees increase with payroll growth.
Flat Fee Per Employee
In this model, the PEO charges a fixed fee per employee. The price might range from $100 to $150 per employee each month, remaining consistent at all times.
The flat fee per employee model works well for businesses looking for a simple, predictable cost structure, unaffected by salary fluctuations. However, this model can become costly as the workforce grows.
- Ideal for: businesses needing predictable monthly expenses.
- Downside: costs increase as the number of employees grows.
Bundled Service Fees
Bundled service fees provide a set price for a package of services. These PEO costs are commonly based on the company’s size and complexity.
This model is ideal for companies wanting a comprehensive suite of services at a predictable rate. However, it may not be as cost-effective for businesses needing only select services.
- Ideal for: companies needing a full-service HR package.
- Downside: may include services you don’t need, leading to higher costs.
À la Carte Pricing
The à la carte model allows companies to pay for individual services, so they’re only billed for what they use. Pricing varies based on each service selected.
This model is ideal for businesses needing flexibility to select specific services. However, it can become more costly as additional services are added.
- Ideal for: businesses needing only select HR services.
- Downside: costs may rise as more services are added.
Administrative Fees
Some PEOs charge a base administrative fee, typically a fixed monthly or annual rate covering general administrative support. This fee is often combined with other models.
The administrative fee structure is ideal for businesses needing general HR administration, but it can add to costs if combined with other fees.
- Ideal for: companies needing basic administrative support.
- Downside: adds to total costs when combined with other fees.
FAQs: Why Use a PEO and Other Crucial Questions
What is a Professional Employer Organization?
A professional employer organization (PEO) is a service provider that manages HR tasks like payroll, benefits, and compliance, acting as the legal employer while you handle daily management of your employees.
What is CPEO and how does it differ from PEO?
A CPEO, short for Certified Professional Employer Organization, is a PEO that has been certified by the IRS, meeting stricter standards for financial stability, tax compliance, and regulatory requirements. The CPEO certification offers additional assurance that the organization will manage payroll taxes and other responsibilities in full compliance with federal laws.
What does a Professional Employer Organization do?
A range of services typically include PEO accounting, payroll processing, benefits administration, compliance assistance, risk management, HR consulting, and employee onboarding/offboarding services. By handling these administrative HR tasks, PEOs allow businesses to focus on growth while ensuring legal compliance and providing employees with competitive benefits.
What does managing HR look like before and after partnering with a PEO?
Before using a PEO, HR teams often spend significant time managing compliance, payroll, and employee benefits in-house. For the in-house teams, it means high workloads and potential compliance risks. In contract, after partnering with a PEO, businesses benefit from streamlined HR functions, reduced compliance risks, access to better benefits, and the ability to focus much more time on strategic initiatives.
How much does a PEO cost?
The cost of working with a PEO usually falls into two models: a percentage of payroll or a monthly flat fee per employee. This investment covers payroll, compliance, benefits, and other HR services, often providing valuable cost savings compared to in-house HR management.
Do I need a PEO and what types of businesses benefit most from it?
Small to medium-sized businesses, high-growth companies, and those expanding internationally benefit most from PEO services, as they gain access to cost-effective HR solutions, competitive benefits, and streamlined compliance in diverse markets. Industries with complex regulations, like healthcare or finance, also find value in PEO expertise.
How does partnering with a PEO affect control over your employees?
While PEOs handle administrative functions, such as payroll and benefits, businesses retain full control over daily employee management, performance expectations, and company culture. The PEO becomes the employer of record for compliance purposes, but operational control remains with the business.
How secure is your company’s data when working with a PEO?
Reputable PEOs implement robust data security measures, such as encryption, limited access, and compliance with data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA), to safeguard client information. When selecting a PEO, verify their data security protocols to ensure alignment with your company’s privacy standards.
How to choose a PEO and what should you consider during the selection?
Choosing a PEO might seem challenging; however, with the right set of criteria, making the right choice is not as hard as it seems. Consider their certifications, industry experience, geographic coverage, pricing structure, and overall communication principles, to name a few. Also, first and foremost, they should be a partner you feel comfortable and confident to work with.
How to find a PEO that would match your business needs?
You can find a PEO that matches your business needs by exploring reputable online directories like NAPEO, PEOcompare, and ADP Marketplace, or by consulting with industry associations and business networks for recommendations.
How can a Professional Employer Organization Company help reduce HR-related risks?
A PEO mitigates HR-related risks by keeping up with legal changes, managing compliance, offering best practices in HR policy. Also, PEO workers compensation and unemployment claims are a part of their service offerings. This expertise reduces the likelihood of non-compliance fines and employment-related liabilities.
Is your business still liable for employment-related issues if you partner with a PEO?
While a PEO reduces your HR compliance risk, your business still holds full responsibility for direct management and workplace conduct. Liability is shared, meaning the PEO handles administrative aspects while you manage day-to-day employee interactions and operational decisions.
Achieve seamless workforce management with PEO – saving time and resources while staying focused on your core business!

Yaryna is our lead writer with over 8 years of experience in crafting clear, compelling, and insightful content. Specializing in global employment and EOR solutions, she simplifies complex concepts to help businesses expand their remote teams with confidence. With a strong background working alongside diverse product and software teams, Yaryna brings a tech-savvy perspective to her writing, delivering both in-depth analysis and valuable insights.





